A 3D laser cutting robot system is developed to laser cut three-dimensional profiles and consists of an industrial robot (usually with 6 axes) with a 3D laser cutting head mounted at the end of the robotic arm.
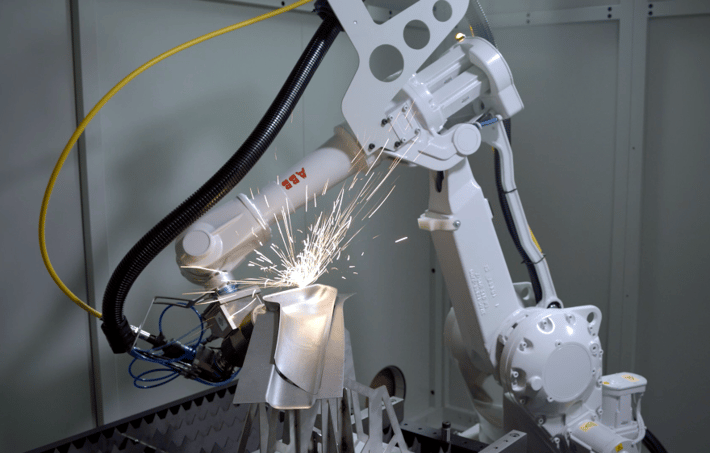 Example of deep drawn material cut with LT360
Example of deep drawn material cut with LT360
Besides the robot and the 3D laser cutting head, the system needs other components:
- Laser source
- Assist gas delivery system
- Enclosure
Laser source
The most common type of laser technology for this application is fiber laser for two main reasons:
- Laser beam transport along an articulated system, such as a 6-axis robot, is easier if carried out through an optical fiber.
- Machined parts (usually bent tubes, molded, hydroformed or deep-drawn parts) have limited thickness, usually less than 6 mm (.24”), and are made of a wide variety of materials: stainless steel, copper alloys, aluminum, titanium, etc.
The thinner material thickness of 3D components requires a lower power laser when compared to sheet metal cutting systems. In general, for a 3D laser cutting machine, both with robot or 5-axis CNC, the power source is usually from 1 kW to 3 kW.
Assist gas delivery system
A laser cutting robot system also needs a system to deliver assist gas.
It is a good rule to choose manufacturers that allow more than one line for different types of gas: nitrogen, oxygen, etc.
Enclosure
The laser wavelength of fiber laser sources is different than CO2 sources and requires certain safety precautions. As a matter of fact, when processing material with a fiber laser, a certified safety enclosure is needed for operator protection.
Companies dedicate time and attention in the design of standardized enclosures. Pre-engineered solutions benefit the end-user with lower costs, quicker delivery, and faster installation times.
The initial investment cost are lower, when compared to customized robotic 3D laser cutting systems, and allow you to start-up production sooner. Whereas, customized systems tend to have longer leads times and higher costs as a result of the design engineering time and safety certification requirements.
Find out more about the benefits of standardized solution in robot 3D laser cutting.
Other components necessary to the system are: the chiller, to cool the laser source, and the fume extractor, that sometimes must be equipped with an upstream distribution system for fume and dust removal.
Robotized laser cutting systems consist of many components: that is why, with the intent of reducing footprint, some manufacturers are developing systems which are extremely compact, but also highly flexible.
Sectors where a 3D laser cutting robot can be used
Similarly to the 5-axis laser cutting systems, the 3D laser cutting robots are becoming widely used in many application sectors.
Even if application sectors for both these technologies are virtually the same, there are real differences.
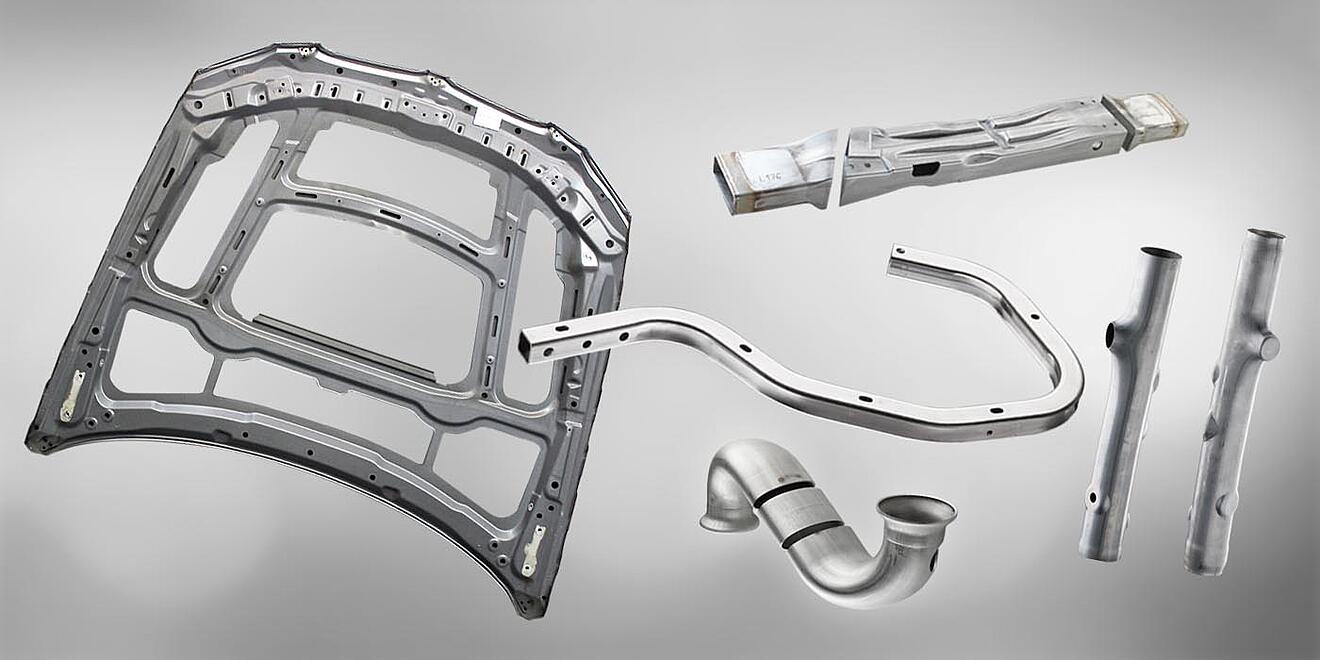

Automotive, motorcycle and aerospace
In sectors like automotive, motorcycle and aerospace, 3D modelling and FEM analysis has changed how parts are designed and manufactured. A considerable number of conventional mechanical parts have been replaced by complex three-dimensional profiles such as bent, hydroformed, deep-drawn, molded, die-cast tubes or pre-welded assemblies. There is a strong focus to design lighter-weight components and reduce number of parts an assembly is made up of, in order to yield better material utilization and achieve increased performance.
Using a robot on these type of parts could be a valid solution to the problem of the geometrical complexity of the part: thanks to the 6 axes of the robot, the 3D laser cutting head can freely reach any point on the part.
Contractors
Another sector where 3D laser cutting systems may be used is that of contractors.
Actually, the use of robots in this sector is still very limited, mainly due to a production flexibility problem, an essential quality for a contractor.
In order to have a 3D laser cutting robot system suitable for this type of production it should be easily programmable, have the ability to set up the part program directly in the machine simply and quickly and the system should be easily accessible.
Taking these factors into consideration, some machine tool and 3D laser cutting system manufacturers have developed compact and turnkey systems for 3D laser cutting with robots.
A robotic solution is able to perform highly complex cutting processes and change production rapidly, providing the flexibility contractors need.
Can a laser cutting robot system offer flexibility? And how?
How to choose a laser cutting robot system which is also flexible? Take into account the following key points:
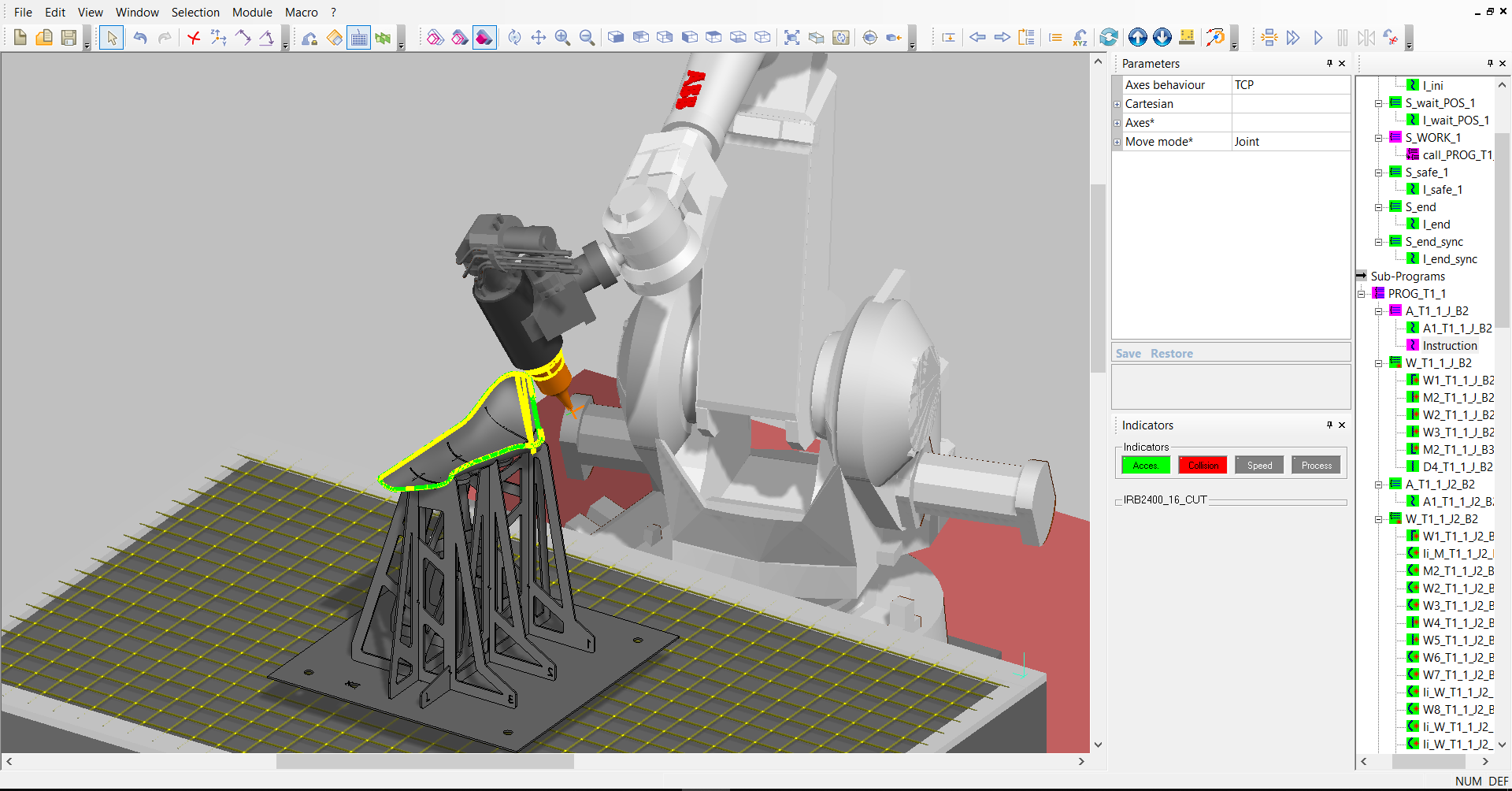 ARTCUT: CAM software for programming laser cutting on 3D workpieces
ARTCUT: CAM software for programming laser cutting on 3D workpieces
Programming software
To quickly program a new operation, the software must be able to:
- Program a new production batch off-line, while the machine is processing a different batch.
- Import 3D files from third-party CAD software.
- Quickly identify cutting paths.
- Identify and solve potential constraints and improve the work cycle in a simple and intuitive manner.
- Simulate your work cycle and start production safely.
Setting up directly in machine
Once the program has been developed offline, it is assigned to the machine post-processor. A flexible system allows you to carry out many changes directly in machine: this is essential to develop prototypes or small batch productions.
A flexible laser cutting system automatically optimizes cutting parameters based on a number of factors, including cutting speed, thickness, type of material to be cut, and 3D laser cutting head inclination.
How can a greater freedom improve your production?
The 6 degrees of freedom of the robot
One of the strengths of using a robot is the greater freedom offered by its 6 axes of motion. This allows the system to:
- Increase the feasibility of the parts as the 6 axes allow the 3D laser head to reach any direction in space.
- Increase speed because 6 axes increase the number of possible rapid paths and reduce part repositioning.
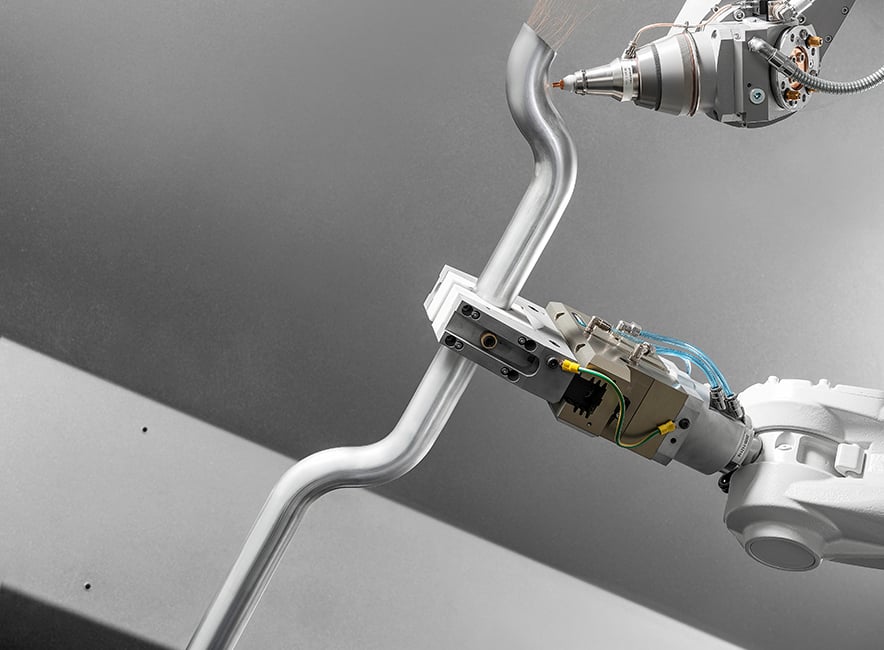
Then, there are solutions that provide a much greater number of freedom levels. The most efficient is with the use of a second robot to manipulate the part, an ideal solution when you need to perform 3D laser cutting on hydroformed parts, bent tubes or other type of closed profiles without manual repositioning.
What are the selection criteria for a 3D laser cutting robot system?
Below is a list of key elements that will help you understand if a 3D laser cutting robot system is suitable for you.
Are you working with complex three-dimensional profiles?
Molded, deep-drawn, hydroformed, die cast parts, bent and hydroformed tubes and any three-dimensional complex profiles are suitable for a 3D laser cutting robot system.
Part volumes shouldn’t be your only consideration
To justify the costs of a 3D laser cutting robot system and accelerate ROI, it is necessary to evaluate the specific production volumes carefully.
This evaluation should also take into account that flexibility offered by the system plays a key role.
Consider programming and set-up time. Choosing a system that allows you to start production rapidly with an offline CAM software and intuitive machine interface, is important to save time.
A flexible system will allow you to be more competitive, to reduce machine production set-up and estimate times. Even if the single production batches are small, you can rapidly change production or develop new prototypes, thus obtaining, in a relatively short period, the volumes necessary for the return on investment.
Why enter into the world of 3D laser cutting with a robotized laser cutting system?
For those who wish to enter into the world of 3D laser cutting, choosing a robotized system could be the ideal option:
- Lower average cost compared to 5-axis laser cutting systems.
- The robot is an independent component that, in future, could be used for other machining processes or resold.
- The system can be expanded with additional material handling or secondary processes to manage future production growth.


