The use of metal tubes in manufacturing is a long-established practice. Every year, millions of tons of metal tubes – of all sizes, thicknesses and shapes – are produced for the most diverse sectors.
Brief history of metal tubes and their use
The first trace of the use of metal tubes was discovered in China around 2000 B.C. for transporting water from one site to another.
The Ancient Romans, in relatively more recent times, used metal pipes for the same purpose. Evidence of metal piping used on a wide scale for distributing water to houses and in aqueducts dates back to the 3rd century B.C. These great works of human ingenuity sustained the development of all the most important cities of the Roman Empire for centuries.
In those days, tubes were made by folding a sheet of lead and sealing it mechanically in the longitudinal direction with a sort of continuous riveting technique.
Since then, metal tube and manufacturing methods have evolved. The pivotal turning point came about in the 1800s with a new awareness of its potential in industries and manufacturing. The invention of the first lighting gas distribution system in the city of London dates back to 1815.
Initially made by joining together the barrels of obsolete muskets, the advantages of the metal piping were immediately obvious and set off a race to improve methods for manufacturing increasingly long elements.
Numerous processes were developed and perfected for making welded tubes: seamless tubes or tube from piercing solid bars along their entire length. It was only in 1911 that the first continuous tube manufacturing plant was created and the foundation of the modern tube mills as we know it today.
Initially, only straight tubes, mechanically cut to size, were made. The invention of bending methods (in the mid-1800s) was another great leap forward on the evolutionary path of humanity.
Until then, oil was transported from extraction wells to railway stations on horseback in barrels (which is why oil is measured in barrels still today), but the construction of bent tubes made it was possible to build the first oil pipelines and further boost scientific and technological progress.
More recently, mild steel, stainless steel (known since 1912), aluminum, copper, brass and other alloys have become increasingly popular for tube making with advantages in the most diverse industries.
.
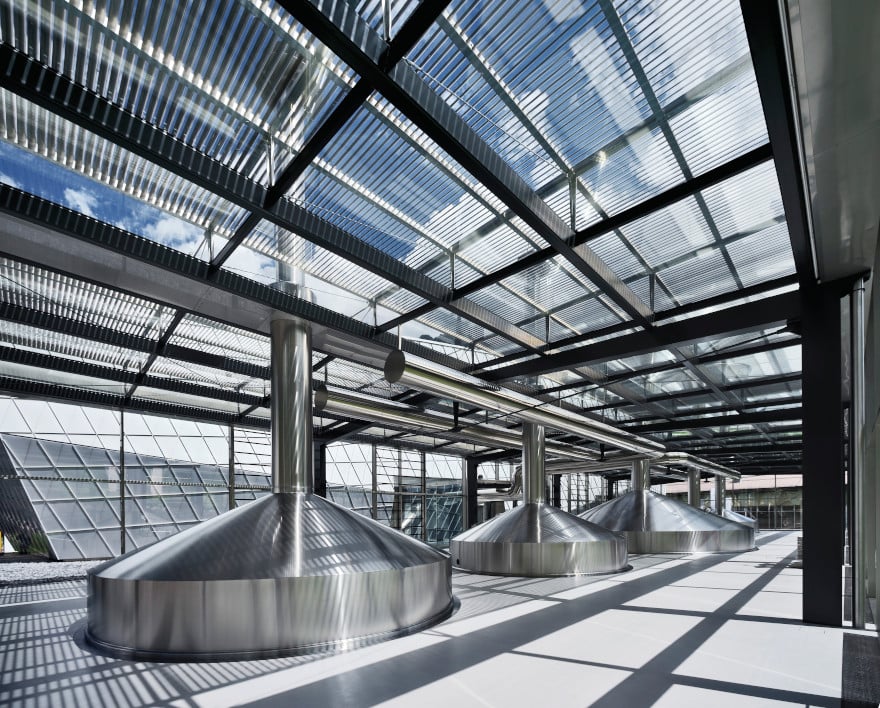 Production facilities of a newly developed brewery near Merano
Production facilities of a newly developed brewery near Merano
Characterized by being lightweight, sturdy and relatively affordable, in addition to coming in a remarkable variety of dimensions, shapes and thicknesses, metal tubes have become indispensable for many applications.
Tubes range from the tiniest diameters (microns) for medical needles to the large and heavy construction steel profiles for structural applications. Round, square, rectangular, H-sections, IPE-sections and unique special sections have brilliantly solved problems in terms of cost reduction and extension of the functions performed by a single component.
The use of special section tubes, characterized by complex geometries and sometimes variable thickness, is becoming more and more prevalent.
This has been promoted by recent developments in tube mill technologies to make tubes to the customers' specifications (backed by the developments in the metallurgical industry for making metal alloys with chemical and physical properties capable of preventing cracking and stretching during forming) and by the availability of processing plants capable of effectively processing and handling these special sections (loading, handling, controlled unloading) to achieve sufficient production rates and overall reliability to make the entire process economically viable
.
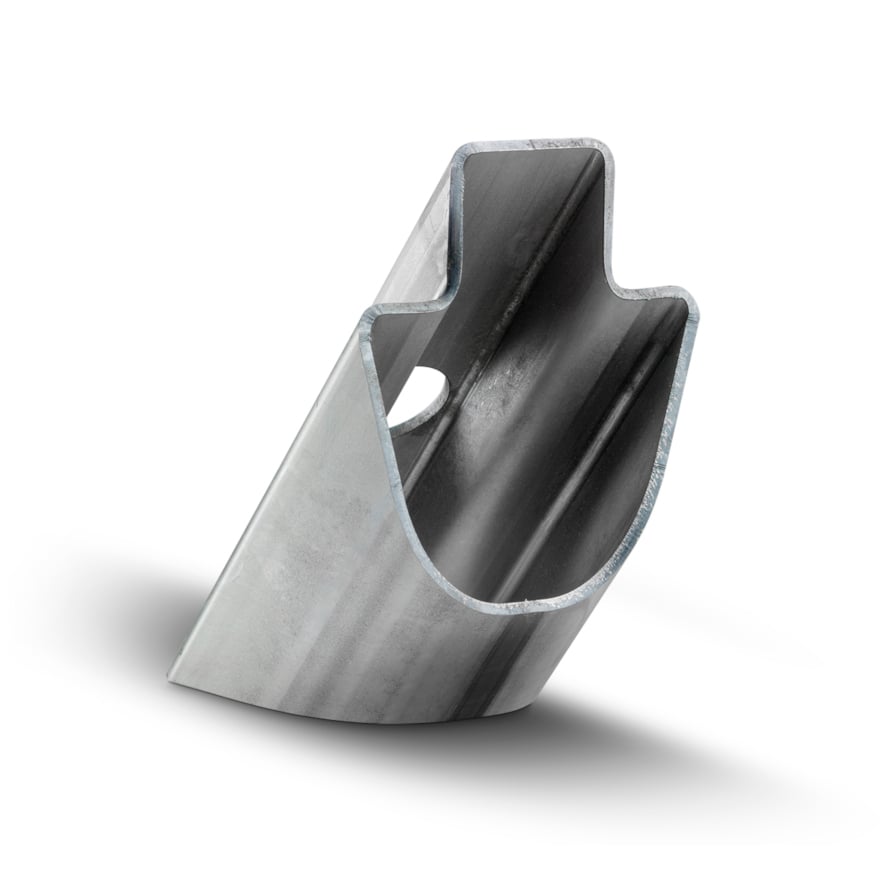 Special section tube cut with Lasertube system BLM GROUP.
Special section tube cut with Lasertube system BLM GROUP.
However, the worldwide production of metal tubes is also growing steadily. Since 2009 (the year of the great recession), production has risen, with China utilizing close to 60%.
Some important areas of use of metal tubes
Some of the many industrial sectors that make extensive use of metal tubes are:
Cars, motorcycles and industrial vehicles
The automotive sector, which in turn is broken down by many adjoining sectors – from light vehicles, such as motorcycles, to large industrial vehicles, earth-moving and agricultural machines – covers a percentage of world demand for tubes around 15% and rising.
Here, high-strength steels are increasingly popular as a result of meeting lightweighting and strength requirements.
Traditionally difficult to machine, laser cutting is the ideal solution for processing high-strength steelr. Laser effectiveness is not impacted by the hardness of these alloys different to that of traditional steels, as opposed to mechanical cutting, which is burdened by wear and tool life (as well as decreased productivity rates).
Find out more about modern laser cutting applications in the production of commercial vehicles
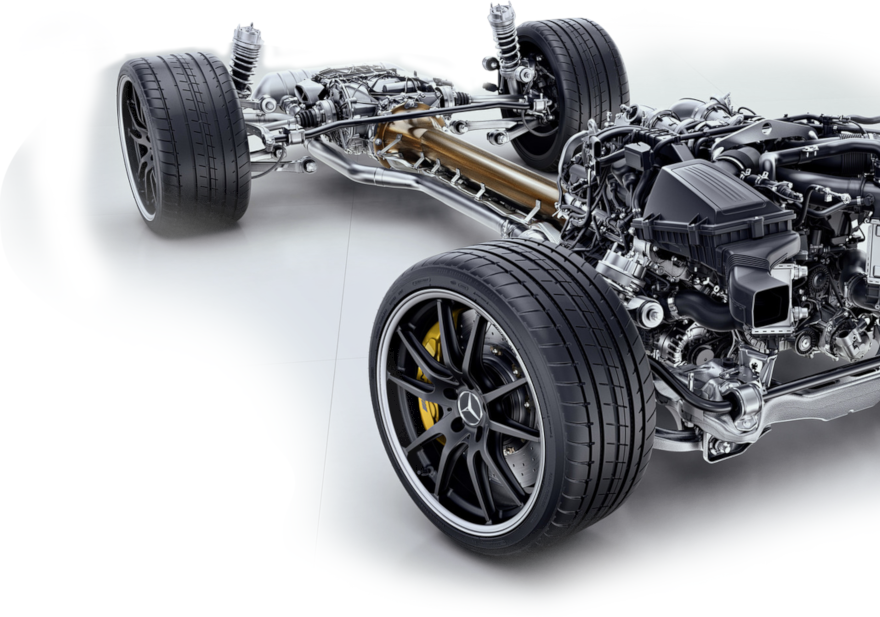 In the automotive industry, high-strength steel tube components are increasingly strongly, because they meet the need for weight reduction and strength.
In the automotive industry, high-strength steel tube components are increasingly strongly, because they meet the need for weight reduction and strength.
Architecture and construction
The construction sector is equally promising in terms of demand and use of steel tubes and profiles. In particular, it accounts for 35% of steel consumption in Europe and over 40% in the USA alone.
The reasons that make steel increasingly preferable to concrete are cost-effectiveness, appearance and, most importantly, sustainability.
Learn more about the benefits of steel construction
Also in this sector, laser cutting is widely applied for its unquestionable, major advantages. The final precision of the parts avoids the need to adjust the measurements of the tubular components during installation, while the absence of thermal alterations to the cut surfaces make them ready to be welded, with no need for preparatory alterations with abrasive tools.
Furniture and design
The furniture sector was one of the first adopters of tube manufacturing for the level and variety of use, but new niches of application are discovered year over year.
With the availability of increasingly sophisticated machining technologies, ever more daring designs are found with tighter tolerances obtained with aesthetic results that amply pay off the complexity of the manufacturing process. Precise supports between tubes that can be welded without filler material, tubular frames with complex geometries, and the replacement of traditionally created products with new technologies mean being able to meet the general trend for customization and differentiation taken to the extreme.
In this case, sustainability and cost-effectiveness derive from the ability of the production process to be quickly reconfigured to switch from one batch to the next, maintaining constant levels of productivity, continuity and efficiency.
From this point of view, once again, laser cutting is the preferred method among manufacturers, precisely because of its flexibility and its unparalleled production rates with the result of keeping the costs of each piece down.
But furniture also means products for city décor and outdoor use, fitness equipment, office furniture, and so forth.
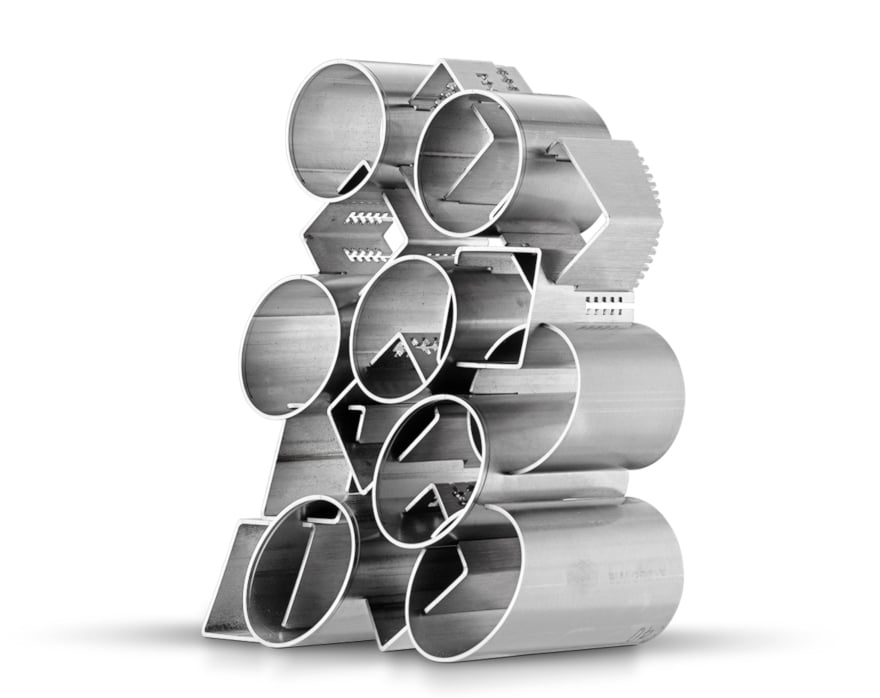 Photo holder made with round and square tubular elements cut with a Lasertube LTFIBER EVO system.
Photo holder made with round and square tubular elements cut with a Lasertube LTFIBER EVO system.
Energy
The overview of the most promising fields of application cannot come to a close without mentioning the energy sector. For energy generation, there are many installations of solar panels that require tubular steel structures (usually galvanized) for installation, while another prime example for energy consumption is that of the HVACR (heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration) sector. The latter linked to the construction sector is also a constantly growing field of application with high innovative potential. Just think of the increasing demand for - smarter and energy-efficient devices.
Manufacturing processes involving many tube processing technologies, whose overall efficiency can also be sought in the synergy that the various technologies can offer. A production process that manages batch tracking and synchronizes the various phases of metal tube processing. First of all, those involving laser cutting and bending technologies, which bring about important mutual benefits in determining the start-up time of each new batch and the risk of generating waste.
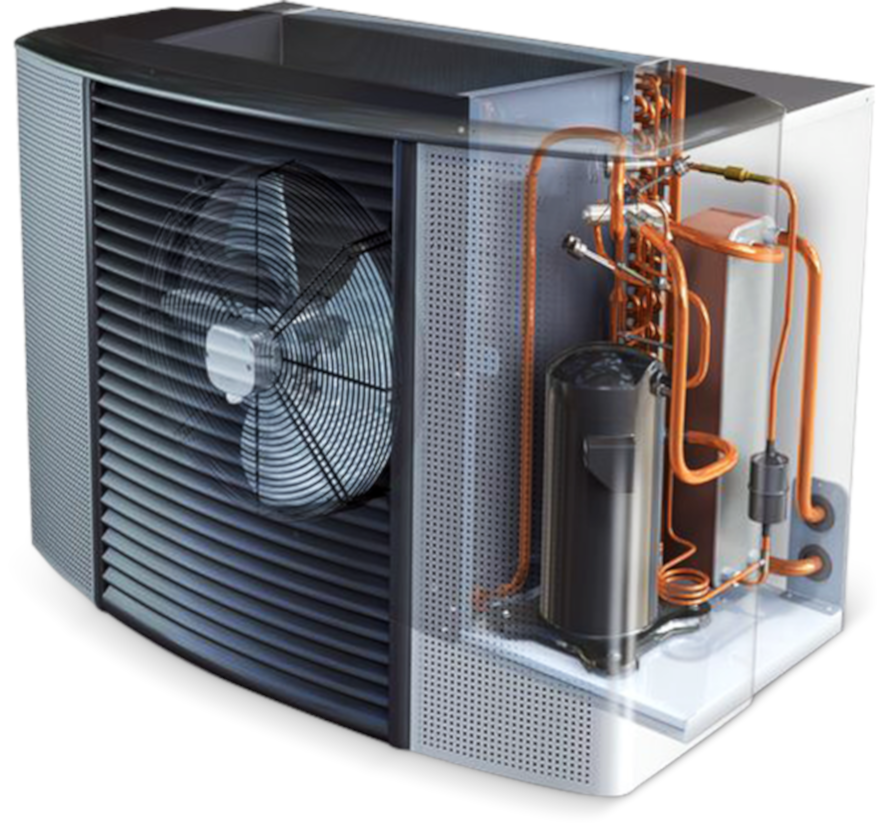 Industrial air conditioning system.
Industrial air conditioning system.
Conclusions
There are a multitude of metal tube applications. Each one has its unique requirements for production: geometry, precision, reliability, automation needs, productivity, and most importantly, the manufacturing technology used to meet these requirements.
To achieve the highest level of competitiveness and ensure your business objectives are met, it is crucial to work with a skilled and reliable supplier with the most suitable equipment. BLM GROUP can help you reach near and long-term goals.


