The precision and technological features of laser cutting are opening new perspectives in the production of welded joints for the structural applications, making it possible to create complex geometry connections with greater accuracy and speed than in the past.
Manufacturers are called to tackle a wide variety of technological and regulatory requirements every day in the transformation of beams and tubes into complex products, such as frames or structures.
The possible operations on large diameter pipes or beams are mainly:
- Processing on the end of the tube, generally consisting of cutting to size, notching for inserting joints or fittings of various types, chamfers or teeth for facilitating post assembly and welding operations
- Processing along the central part, generally consisting of lightening cuts, notches for passing pipes, geometries of various types for intersecting other beams, tubes or components
Particularly important for the constructions sector is the creation of joints. The fundamental connecting elements between beams and/or pipes are being constantly developed in steel constructions.
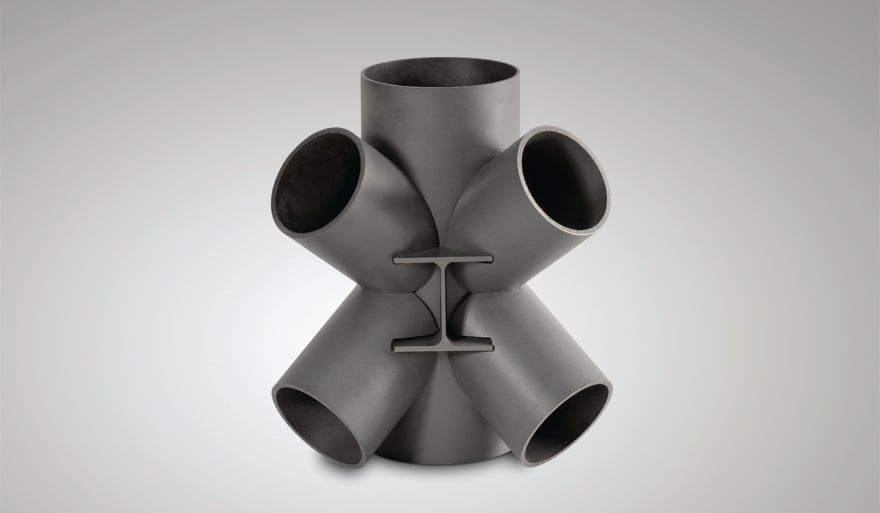 HE beam and tube joint created with LT24, the laser cutting system for large-size tubes and profiles made by BLM GROUP.
HE beam and tube joint created with LT24, the laser cutting system for large-size tubes and profiles made by BLM GROUP.
The main advantages of laser cutting in this field include:
Material savings and ease of assembly
The precision and versatility offered by laser cutting make it possible to create the most varied tube and profile interlocking solutions to improve mechanical strength, but also to reduce assembly complexity and save time.
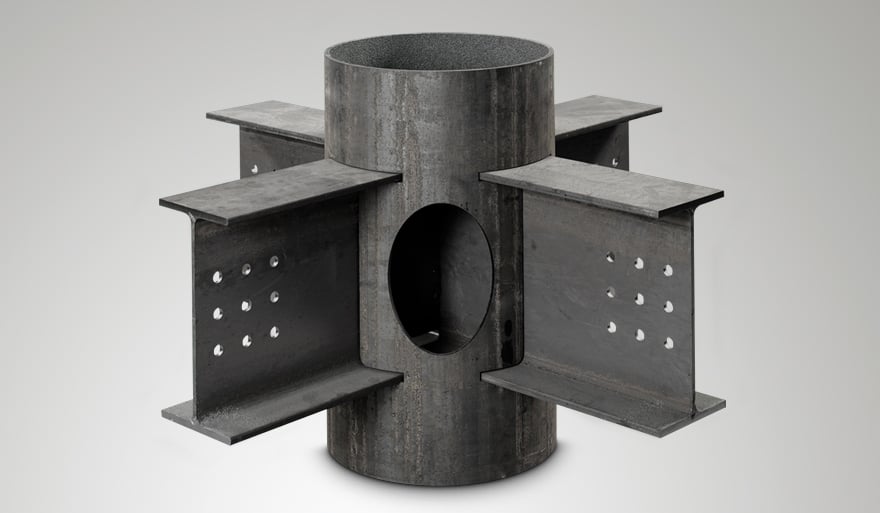 Joint made with the LT24 laser cutting system for large-size tubes and profiles by BLM GROUP.
Joint made with the LT24 laser cutting system for large-size tubes and profiles by BLM GROUP.
The joint shown above is a practical example. Made without using bolts, rivets, or other connecting elements, it allowed a saving of 63% material weight and 62% production cost.
The following picture compares the same type of joint made using plates and bolts (picture a) and the individual construction elements of the joint made using an LT24 laser cutting system (pictures b, c, d).
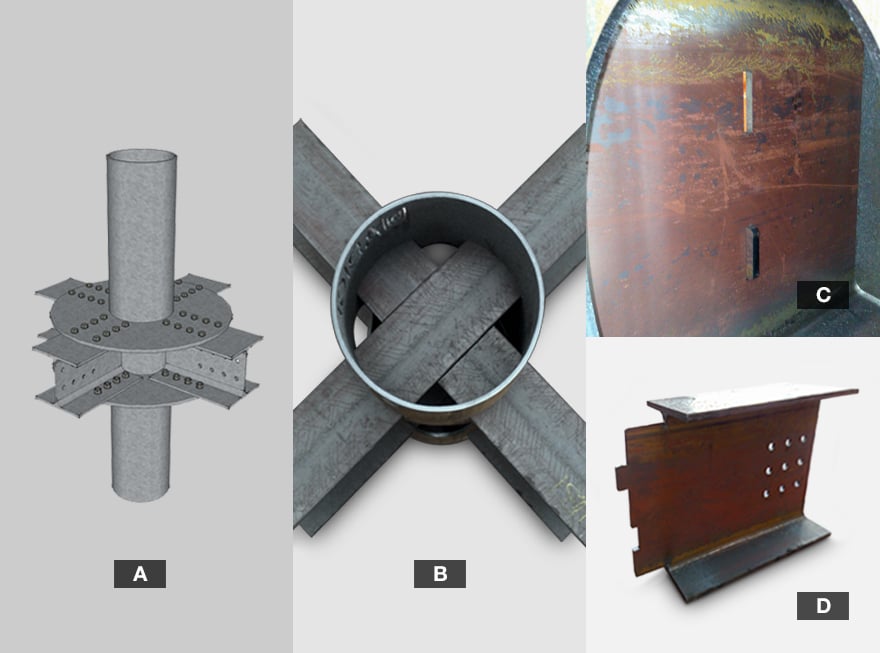 Drawing of the joint made using bolts and plates (a), top view of the joint made with LT24 laser cutting system for large-size tubes and profiles (b), processing on IPE beam that passes through the joint (c), processing of the end of the tube on the other two IPE beams (d).
Drawing of the joint made using bolts and plates (a), top view of the joint made with LT24 laser cutting system for large-size tubes and profiles (b), processing on IPE beam that passes through the joint (c), processing of the end of the tube on the other two IPE beams (d).
Accuracy and quality
Using a 3D laser cutting system means that the required operations can be carried out with greater precision than with plasma and oxyfuel cutting technologies. It produces smooth, burr-free cutting edges with an extremely small heat affected zone*.
This avoids the need for grinding operations on the workpiece and ensures that the various components of the structure are ready for assembly and welding, saving time and energy.
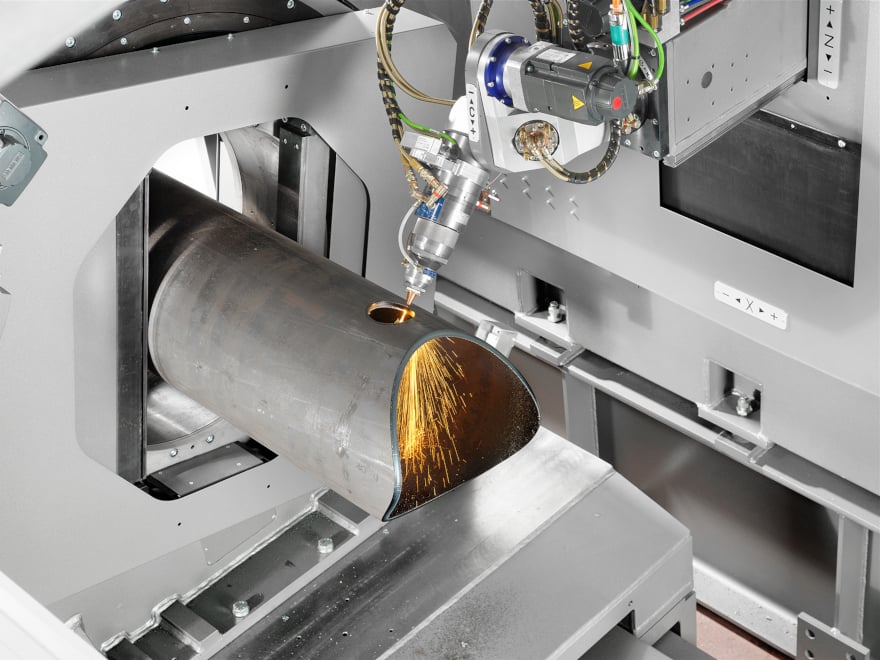 Preparation of a tubular element for a welded joint on the LT24 BLM GROUP tube laser cutting system.
Preparation of a tubular element for a welded joint on the LT24 BLM GROUP tube laser cutting system.
Reducing the heat affected area means reducing the part of the material whose chemical or mechanical properties may have transformed as a result of temperature change.
Furthermore, the most advanced laser cutting systems have features designed to optimize cutting parameters automatically. This not only benefits productivity and process robustness, but also produces the best cutting quality regardless of the operator's experience.
Find out more about these types of installations
|
*Heat affected zone The heat-affected zone is the part of steel whose chemical and mechanical properties have been modified by the intense heat generated in a thermal cutting processes (these processes take advantage of the fusion or local sublimation of the material to cut the metal). In the case of steel, this rapid change in temperature can generate localized hardening that makes the material harder and more brittle at the same time. It can also cause chemical changes such as oxidation and/or nitriding. The advantages of laser The laser, unlike plasma and oxyfuel, considerably reduces the heat-affected zone due to its technological features and the fact that it concentrates all the beam energy in an extremely small portion of the surface. |
Making ready-to-weld parts in one process
Shielded metal arc welding is currently the only type of welding used on-site and is characterized by the degree of penetration of the filler material according to three types:
- complete joint penetration welding;
- partial joint penetration welding;
- corner seam welding.
Innovative welding technologies, such as robotic laser welding, enable component manufactures for the structural sector to achieve repeatable, high-quality results. One example is the LW-S robotic laser welding system, a compact and highly configurable welding cell perfect for a wide variety of welding joints and components for the light construction and structural sectors – ready to be used on site.
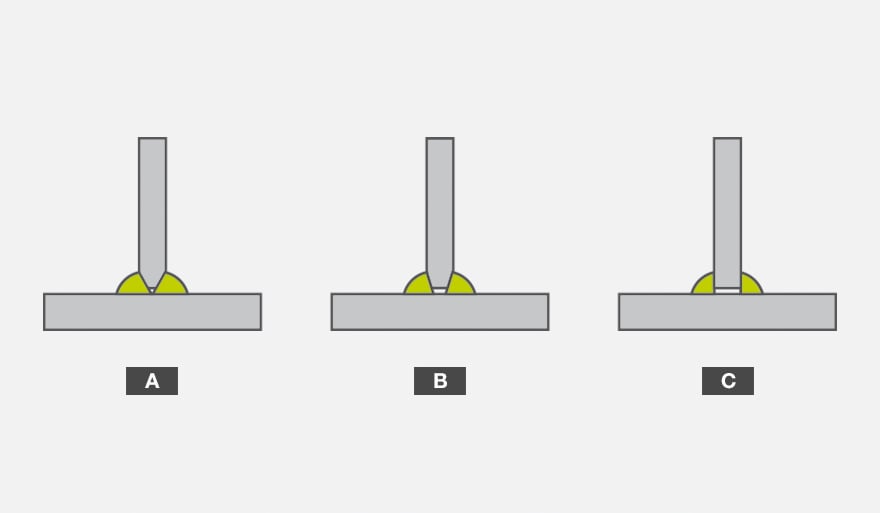 (a) Complete joint penetration welding, (b) partial joint penetration welding, (c) corner seam welding.
(a) Complete joint penetration welding, (b) partial joint penetration welding, (c) corner seam welding.
Although complete joint penetration welding provides the best performance because it does not interrupt the material continuity at any point. If carried out with traditional production systems, it is also the most expensive because experienced operators are required to manually and accurately prepare the edges to be welded. The geometry of the edges according to the established regulatory framework must respect given geometric specifications, such as angle and chamfer depth, shoulder size and mutual distance between the welded edges.
In this context, the use of a 3D laser cutting system is particularly advantageous because the parts are made in a single laser cutting process, cut to specification and ready for welding.
A 3D laser cutting system for large-size tubes or profiles allows the production of chamfers of different inclinations and variable inclination along the entire cutting edge. This makes it possible to keep the chamfer angle within the parameters set by the regulatory framework even when welding between tubes or tubes and/or profiles are not mutually orthogonal.
Furthermore, the variety of geometric shapes that can be made with 3D laser cutting systems for large-size tubes and sections makes it possible to include teeth that can be used to strengthen the joint and simplify the welding process by maintaining the distance between the edges to be joined.
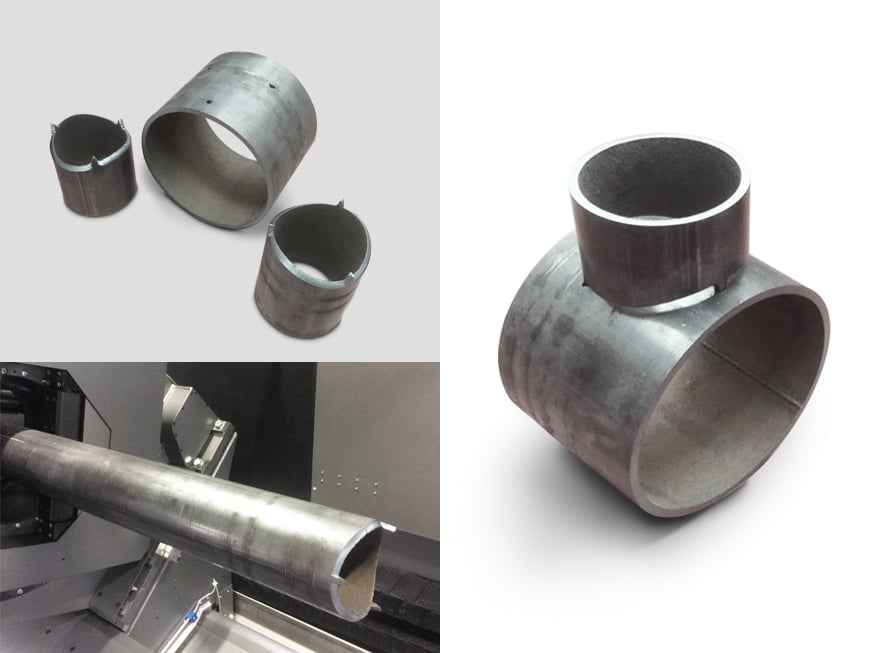 3D laser cutting makes it possible to make chamfers with the correct inclination to optimize the penetration of the filler material during welding, as well as teeth to maintain the positioning of the parts and the distance between the edges.
3D laser cutting makes it possible to make chamfers with the correct inclination to optimize the penetration of the filler material during welding, as well as teeth to maintain the positioning of the parts and the distance between the edges.
Some of these systems have advanced CAD/CAM software tools that provide the user with libraries complete with teeth, joints, and an entire series of features that can speed up the creation of any project.
By using a 3D laser cutting system, the secondary assembly phases are simpler and even the less experienced operators can weld to produce optimal results.
Strong in its many advantages, 3D laser cutting systems for large-size tubes and sections can be used for structural applications and also for agricultural & industrial vehicle manufacturing, shipbuilding, oil & gas, oil rig construction, and power plants.
The system can introduce new standards of quality, flexibility and productivity in a wide variety of applications.


